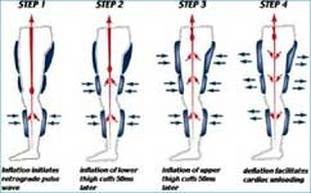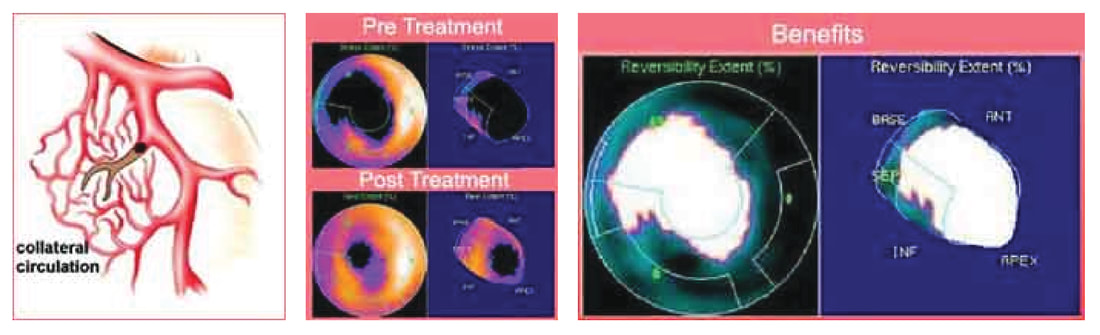
EECP has two potentially beneficial actions on the heart. First, the milking action of the leg cuffs increases the blood flow to the coronary arteries. (The coronary arteries, unlike other arteries in the body, receive their blood flow after each heartbeat instead of during each heartbeat. EECP, effectively, "pumps" blood into the coronary arteries.) Second, by its deflating action just as the heart begins to beat, EECP creates something like a sudden vacuum in the arteries, which reduces the work of the heart muscle in pumping blood into the arteries. Both of these actions have long been known to reduce cardiac ischemia (the lack of oxygen to the heart muscle) in patients with coronary artery disease. Indeed, an invasive procedure that does the same thing, intra-aortic counterpulsation (IACP, in which a balloon-tipped catheter is positioned in the aorta, which then inflates and deflates in time with the heartbeat), has been in widespread use in intensive care units for decades, and its effectiveness in stabilizing extremely unstable patients is well known.